
Cylindrical Roller Bearing
single row, with cage
- Available in various designs
- Higher load ratings than comparable deep groove ball bearings
- Suitable for high speeds

Single row cylindrical roller bearings with cage can absorb higher loads than ball bearings due to the linear contact between rolling element and bearing ring. They are suitable for the absorption of high radial forces while their axial load capacity is limited. The designs differ in number of flanges on the inner and outer ring. Single row cylindrical roller bearings can be disassembled and are easily installed or uninstalled. They are suitable for high speeds, but they only allow angular errors to a limited extent.
Dimensions and Tolerances
KRW supplies single row cylindrical roller bearings with normal tolerance (PN) in accordance to DIN 620-2 (Tolerances for roller bearings) and ISO 492 (Radial bearings - Dimensional and geometrical tolerances). All other deviating or special tolerances must be specified with the order.
Standards
The dimensions of the cylindrical roller bearings are standardised in DIN 5412-1 (Rolling bearings - Cylindrical roller bearings), DIN 616 (Rolling bearings - Dimensions), and ISO 15 (Radial bearings - Boundary dimensions, general plan).
The dimensions of the L-section rings (HJ) are standardised in DIN 5412-1 and ISO 246 (Cylindrical roller bearings, separate thrust collars).
Bearing Design
Single row cylindrical roller bearings with cage are dismountable and non-latching bearings that appear in different designs. The designs differ in number and arrangement of flanges.
Single row cylindrical roller bearings with cage are suitable for the absorption of very high radial forces and can reach high speeds compared to full complement designs. Cylindrical roller bearings can be delivered with cylindrical or tapered bore.
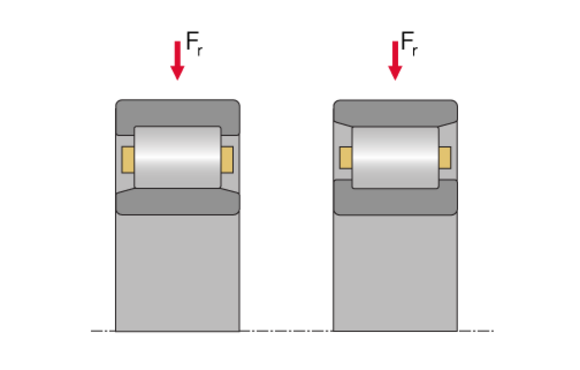
Cylindrical roller bearing, type NU (left) and N (right)
The most common types are NU and N. The outer ring of NU bearings has two integral flanges while the smooth inner ring is designed without flanges. For N bearings, the two integral flanges are located on the inner ring and the outer ring has no flanges. The missing flanges facilitate shaft clearance in axial direction of the housing and lets the bearing function as floating bearing.
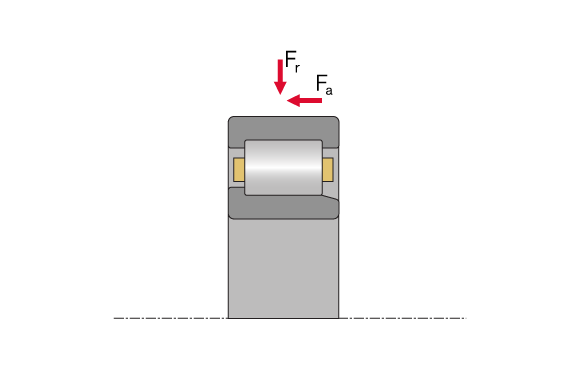
Cylindrical roller bearing, type NJ
In addition to two integral flanges on the outer ring, NJ bearings have an integral flange on the inner ring which facilitates axial clearance in one direction and allow the bearing to be used as supporting bearing.
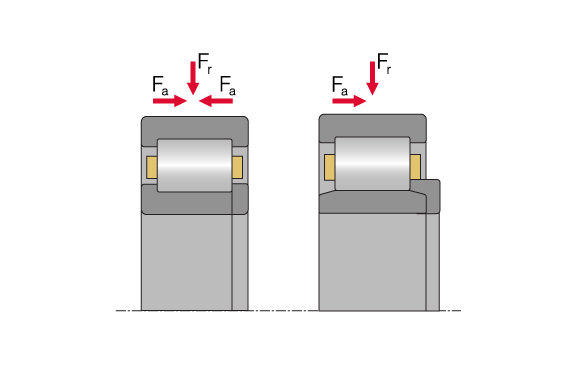
Cylindrical roller bearing, type NUP (left), cylindrical roller bearing type NU with L-section ring HJ (right)
In addition to two integral flanges on the outer ring, NUP bearings have an integral flange on the inner ring and a shoulder ring (P) which in conjunction no longer allow axial clearance and provide for the use as fixed bearing.
By mounting an L-section ring (HJ) on NU bearings, these bearings can also be combined to supporting bearings.

Different types of cylindrical roller bearings
By default, cylindrical roller bearings by KRW are designed with optimised contact areas between rolling elements and raceways. Due to the logarithmic profiling of the cylindrical rollers, damaging edge tension is avoided even with very high loads.
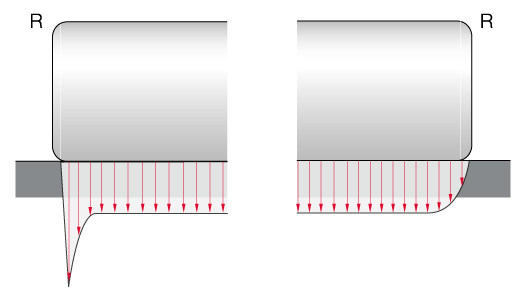
Roller profiling and tension distribution of cylindrical rollers in comparison: without profiling (left), with profiling (right)
Bearing Clearance
KRW supplies single row cylindrical roller bearings in normal clearance (CN) in accordance with DIN 620-4 (Rolling bearing tolerances) and ISO 5753-1 (Rolling bearings - Internal clearance), but they are also available in all clearance classes with restricted clearance or special clearance. Bearing components with a standardised bearing type according to DIN 5412 with identical standard clearance are interchangeable with each other. For clearance classes smaller than CN or restricted clearance classes, an interchange of bearing components is no longer possible because the components must be compatible.
| ||||||||

Cage
By default, single row cylindrical roller bearings by KRW are equipped with a two-piece roller-riding solid brass cage (suffix: M3 or M4). Other cage designs are available on request or chosen for specific applications and labelled accordingly on the bearing.
Special Suffixes
| A | Modified internal design |
| E | Modified internal design, increased capacity design |
| EX | Modified internal design, adapted according to norm, Bearing parts not interchangeable with the previous E version |
| MPAD | Solid brass window cage, rib-guided on outer ring, by special cage pocket geometry of the cage with the rolling elements can be removed from the outer ring |
Compensation of Angular Misalignments
Single row cylindrical roller bearings are of limited suitability for compensation of misalignments. The admissible misalignment between inner and outer ring depends on the bearing size, the internal bearing design, the clearance fit, and the acting of forces and moments. Misalignments cause harmful unwinding of the roller elements and produce additional stresses in the bearing which reduce its operating life.
Speed
KRW distinguishes between kinematic limiting speed nG and thermal reference speed nth. The kinematic limiting speed is a practical mechanical limit value and is based on the mechanical fatigue strength of the rolling bearing as a function of its installation situation and lubrication. The limit speed must not be exceeded even under optimum operating conditions without prior consultation with KRW.
The thermal reference speed represents the equilibrium between the heat generated in the bearing by friction and the heat flow dissipated. It is standardised in DIN ISO 15312 (Rolling bearings - Thermal reference speed).
Admissible Operating Temperatures
The admissible operating temperature of a bearing is limited by cage material, dimensional stability of the bearing components (ball race and rolling elements), as well as lubrication. By default, KRW bearings are stabilised up to 200°C (S1). KRW provides roller bearings for higher operating temperatures on request.
Dimensioning
For dynamically loaded bearings
The service life formula according to ISO 281 L10 = (C/P)p for dynamically loaded bearings requires an equivalent load (P) from constant direction and size. To calculate P, calculation factors and the ratio of axial and radial load are required. This is shown in the following equations.
Equivalent Dynamic Bearing Load P
a) Floating bearings
For a purely radially loaded cylindrical roller bearing acting as a floating bearing, the following applies:
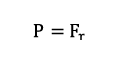
| P | equivalent dynamic load | [kN] |
| Fr | dynamic radial force | [kN] |
b) Fixed bearings
The equivalent bearing service life for axially loaded radial cylindrical roller bearings (cylindrical roller bearings with flanges on the inner and outer ring for axial shaft guidance) depends on the ratio Fa/Fr (axial force / radial force). The equivalent dynamic bearing load can then be determined using the following formula:
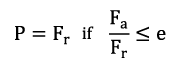
| P | equivalent dynamic load | [kN] |
| Fr | dynamic radial force | [kN] |
| Fa | dynamic axial force | [kN] |
| e | calculation factor, see chart | [-] |
| dimension series | factor e |
| 10, 18, 19, 2, 3, 4 | 0,2 |
| 22, 23, 28, 29 | 0,3 |
If Fa/Fr > e, please consult the KRW Application Engineering Team.
For statically loaded bearings
Dynamic dimensioning loses its validity for bearings rotating at very low speeds (n x dm ≤ 4000 mm/min). The static load safety factor S0 is calculated as follows:
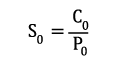
| S0 | static load safety factor | [-] |
| C0 | static load rating (from bearing chart) | [kN] |
| P0 | equivalent static bearing load | [kN] |
| n | bearing speed | [min-1] |
| dm | mean bearing diameter [dm = (D+d)/2] | [mm] |
Static load capacity
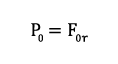
Admissible dynamic axial load capacity
The axial load capacity of a cylindrical roller bearing with flanges on the inner and outer ring depends primarily on the heat balance of the bearing and thus on the lubrication and friction conditions. For axial bearing loads there always must be a load-carrying lubricant film on the contact area between the front side of the rolling element and the flange. Before using the formula below, the following operating conditions must be met:
- viscosity ratio K ≥ 2
- max. misalignment between inner and outer ring ≤ 1 angular minute
- For grease lubrication, attention must be paid that there is an axial load that is changing in load direction so there always is enough lubrication at the contact point.
- EP additives are recommended
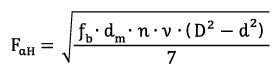
| FaH | admissible hydrodynamic stress limit | [N] |
| fb | for bearings with cage: 0.0048 | [-] |
| dm | mean bearing diameter | [mm] |
| n | speed | [min-1] |
| v | operating viscosity | [mm2/s] |
For cylindrical roller bearings subject to high axial loads, the loaded flanges must be supported over the entire flange height. The height of the flanges can be taken from the bearing charts.
Minimum Radial Load
A minimum load is required for the reliable operation of a rolling bearing. If the minimum load is not reached, slippage may occur. The minimum radial load for cylindrical roller bearings is roughly assumed to be 1.67% of the static load rating C0 of the bearing. If the value falls below this value, please consult KRW Application Technology.



