
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
full complement, multi row
- Very high radial load ratings in small installation space
- High radial rigidity
- Only suited for low speeds

Multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings can absorb highest radial forces thanks to the highest possible number of rolling elements. The bearings are very rigid radially and especially suitable for space-efficient constructions. Speeds of full complement bearings are distinctly lower than those of cylindrical roller bearings with cage. Multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings can be disassembled and suitable for low speeds. They do not allow angular errors.
Dimensions and Tolerances
KRW supplies multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings with normal tolerance (PN) in accordance to DIN 620-2 (Tolerances for roller bearings) and ISO 492 (Radial bearings - Dimensional and geometrical tolerances). All other deviating or special tolerances must be specified with the order.
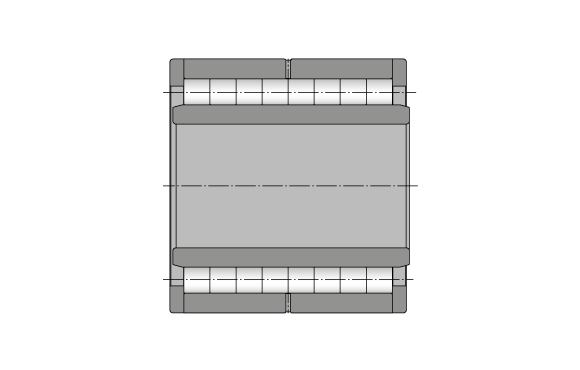
Bearing Design
Multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings are dismountable and non-latching bearings that KRW produces in the bearing type NNU...V.
Multi row full complement NNU...V bearings consist of six rolling element rows, two loose shoulder rings on the outer ring and an inner ring without flanges. The missing flange facilitates shaft clearance in axial direction of the housing and lets the bearing function as floating bearing.
Multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings are suitable for the absorption of highest radial forces and offer especially high radial rigidity.
Attention: Full complement cylindrical roller bearings are not compulsively designed as latching. The rolling elements can consequently fall out during disassembly.
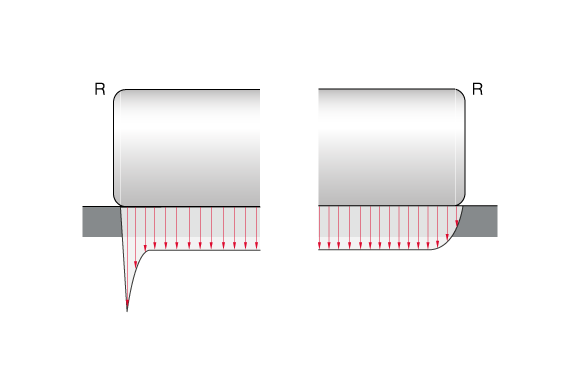
Left without profiling, right with profiling
By default, cylindrical roller bearings by KRW are designed with optimised contact areas between rolling elements and raceways. Due to the logarithmic profiling of the cylindrical rollers, damaging edge tension is avoided even with very high loads.
Bearing Clearance
KRW supplies multi row cylindrical roller bearings in normal clearance (CN) in accordance with DIN 620-4 (Rolling bearing tolerances) and ISO 5753-1 (Rolling bearings - Internal clearance), but they are also available in all clearance classes with restricted clearance or special clearance. Bearing components with a standardised bearing type with identical standard clearance are interchangeable with each other. For clearance classes smaller than CN or restricted clearance classes, an interchange of bearing components is no longer possible because the components must be compatible.
| ||||||||
Special Suffixes
| V | full complement bearing (without cage) |
| VH | full complement bearing (without cage), self-retaining |
Compensation of Angular Misalignments
Multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings are not suitable for compensation of misalignments. Misalignments cause edge stresses between rolling elements and raceways and produce additional stresses in the bearing which reduce its operating life.
Speed
The kinematic limit speed nG was determined empirically and must not be exceeded even under optimum operating conditions without prior consultation with KRW.
The DIN ISO 15312 (Rolling bearings - Thermal speed rating) does not specify a thermal speed rating nth for these bearings.
Admissible Operating Temperatures
The admissible operating temperature of a bearing is limited by cage material, dimensional stability of the bearing components (ball race and rolling elements), as well as lubrication. By default, KRW bearings are stabilised up to 200°C (S1). KRW provides roller bearings for higher operating temperatures on request.
Dimensioning
For dynamically loaded bearings
The service life formula according to ISO 281 L10 = (C/P)p for dynamically loaded bearings requires an equivalent load (P) from constant direction and size. To calculate P, calculation factors and the ratio of axial and radial load are required.
Equivalent Dynamic Bearing Load P
For a purely radially loaded cylindrical roller bearing acting as a floating bearing, the following applies:
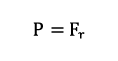
| P | equivalent dynamic load | [kN] |
| Fr | dynamic radial force | [kN] |
For statically loaded bearings
Dynamic dimensioning loses its validity for bearings rotating at very low speeds (n x dm ≤ 4000 mm/min). The static load safety factor S0 is calculated as follows:
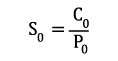
| S0 | static load safety factor | [-] |
| C0 | static load rating (from bearing chart) | [kN] |
| P0 | equivalent static bearing load | [kN] |
| n | Speed | [min-1] |
| dm | mean bearing diameter [dm = (D+d)/2] | [mm] |
Static load capacity
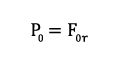
Minimum Radial Load
A minimum load is required for the reliable operation of a rolling bearing. If the minimum load is not reached, slippage may occur. The minimum radial load for multi row full complement cylindrical roller bearings is roughly assumed to be 1.67% of the static load rating C0 of the bearing. If the value falls below this value, please consult KRW Application Technology.



