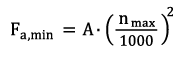Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings
single direction
- Absorption of axial forces from one direction
- Absorption of radial forces
- Available in highest precision for machine tools

Single-sided angular contact thrust ball bearings are high precision bearings and feature angular raceways of shaft and housing washers and a resulting force-transferring contact angle. This contact angle has an angle of 60° and facilitates the absorption of high axial forces as well as radial and combined forces. Single-sided angular contact thrust ball bearings can only absorb axial forces from a single side. Combined with a second mirror-image arranged bearing, the absorption of axial forces from both sides is facilitated. Angular contact thrust ball bearings are very rigid and are suitable for high speed needs, but they cannot compensate misalignments.
Single-sided angular contact thrust ball bearings are not self-latching, so the roller cage assembly and the bearing washers can be installed separately.
Dimensions and Tolerances
KRW supplies angular contact thrust ball bearings in accordance with DIN 620-3 (Tolerances for rolling bearings) and ISO 199 (Thrust bearings - Geometrical product specification (GPS) and tolerance values) in normal tolerance (PN). All other deviating or special tolerances must be specified with the order.
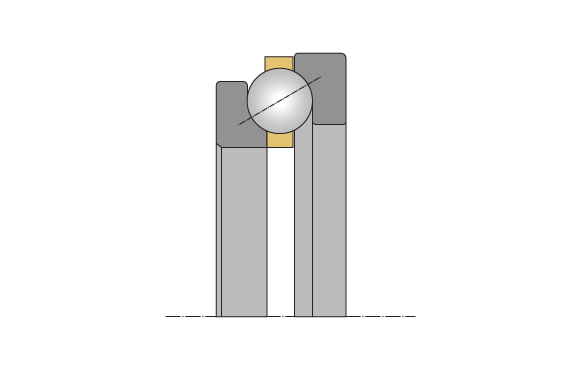
Angular contact thrust ball bearing
Bearing Design
Single-sided angular contact thrust ball bearings are non-latching bearings that can be disassembled. In addition to high radial forces, they can absorb high single-sided axial forces as well as, in combination with a second mirror-image arranged angular contact thrust ball bearing, two-sided axial forces.
For combined bearing sets there is a distinction between O-, X-, or tandem arrangement based on pressure line contact. Bearings in X-arrangement are less suitable for the absorption of moment loads while the O-arrangement is very rigid and only allows small overturning clearance. For tandem arrangements, the pressure lines of two bearings run in one direction which results in only single-sided absorption of axial forces. A double bearing allows the distribution of axial loads which increases the load capacity.
Bearing Clearance
The bearing clearance for angular contact thrust ball bearings is adjusted only after installation according to operating conditions. The temperature-dependent length variation of the operating components must be considered.

Cage
By default, KRW angular contact thrust ball bearings are equipped with a solid brass cage (suffix: M). Other cage designs are available on request or chosen for specific applications and labelled accordingly on the bearing.
Suffixes
Compensation of Angular Misalignments
Angular contact thrust ball bearings are not suitable for compensation of misalignments. Misalignments cause harmful ball movement and produce additional stresses in the bearing which reduce its operating life.
Speed
The kinematic limiting speed nG is a practical mechanical limit value and is based on the mechanical fatigue strength of the rolling bearing as a function of its installation situation and lubrication. The limit speed must not be exceeded even under optimum operating conditions without prior consultation with KRW.
The DIN ISO 15312 (Rolling bearings - Thermal speed rating) does not specify a thermal speed rating nth for these bearings.
Admissible Operating Temperatures
The admissible operating temperature of a bearing is limited by cage material, dimensional stability of the bearing components (ball race and rolling elements), as well as lubrication. By default, KRW bearings are stabilised up to 200°C (S1). KRW provides roller bearings for higher operating temperatures on request.
Dimensioning
For dynamically loaded bearings
The service life formula according to ISO 281 L10 = (C/P)p for dynamically loaded bearings requires an equivalent load (P) from constant direction and size. To calculate P, calculation factors and the ratio of axial and radial load are required.
Equivalent dynamic bearing load Pa
The equivalent dynamic bearing load can be determined using the following formula:

| Pa | equivalent dynamic load | [kN] |
| Fa | dynamic axial force | [kN] |
| Fr | dynamic axial force | [kN] |
The specified values apply to a contact angle of 60°. If the contact angle deviates, please consult KRW Application Engineering.
Für statisch beanspruchte Lager
Bei sehr langsam drehenden Lagern (n x dm ≤ 4000 mm/min) verliert die dynamische Dimensionierung ihre Gültigkeit. Die statische Tragsicherheit S0 errechnet sich nach:
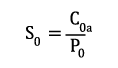
| S0 | static load safety factor | [-] |
| C0a | basic static load rating (from bearing chart) | [kN] |
| P0 | equivalent static bearing load | [kN] |
| n | bearing speed | [min-1] |
| dm | mean bearing diameter [dm = (D+d)/2] | [mm] |
Static load capacity
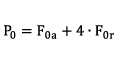
| F0, a | max. axial static load | [kN] |
| F0, r | max. radial static load | [kN] |
The specified values apply to a contact angle of 60°. If the contact angle deviates, consult KRW Application Engineering.
Minimum Axial Load
A minimum load is required for the reliable operation of a rolling bearing. If the minimum load is not reached, slippage may occur. This produces surface damage which leads to premature bearing failure. Angular contact thrust ball bearings are protected against slippage exclusively through a minimum axial load. The calculation for the minimum axial load for angular contact thrust ball bearings is shown in the following formula: