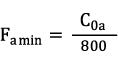Spherical Roller Thrust Bearings
metric
- Compensation of angular misalignments
- Absorption of high axial forces from one direction
- Suitable for medium speeds

Spherical roller thrust bearings can be angularly adjusted and can compensate angular misalignments between shaft and housing due to the concave outline of shaft and housing raceways and the asymmetrical barrel-shaped rollers. They can absorb very high axial forces from a single direction as well as radial forces and are suitable for relatively high speeds despite high loads. Cage, roller cage assembly and shaft washer are self-latching, so they can be assembled separately from the housing washer.
Dimensions and Tolerances
KRW supplies spherical roller thrust bearings with normal tolerance (PN) in accordance with DIN 620-3 (Tolerances for rolling bearings) and ISO 199 (Thrust bearings - Geometrical product specification (GPS) and tolerance values). All other deviating or special tolerances must be specified with the order.
Bearing Design
Spherical roller thrust bearings are non-latching bearings that can be disassembled. The high number of tapered rollers allows a very high axial load from a single direction while the tilted raceways of the bearing washers facilitate a simultaneous radial load. Dependent on the bearing series and size, KRW manufactures spherical roller thrust bearings in two different versions (E and EA) which differ in dimensions of retaining sleeves and shaft washers.
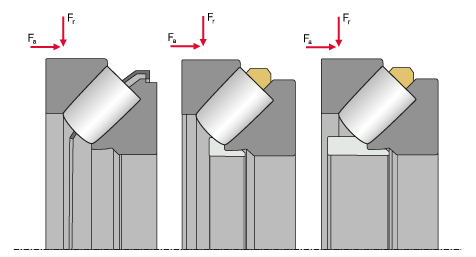
Single direction spherical roller thrust bearing (E version with metal sheet cage, E version with brass cage, EA version with brass cage)
Bearing Clearance
The bearing clearance for spherical roller thrust bearings is adjusted only after installation according to operating conditions. The temperature-dependent length variation of the operating components must be considered.

Cage
By default, KRW spherical roller thrust bearings are equipped with a solid brass cage (suffix: MB). Other cage designs are available on request or chosen for specific applications and labelled accordingly on the bearing.
Compensation of Angular Misalignments
Spherical roller thrust bearings are suitable for compensation of misalignments between shaft and housing washers due to shaft deflections, angular errors and housing deformation. The admissible angular misalignment with static and circulating shaft washer is 1° to 2°. Deviating angles are available on request or custom-designed.
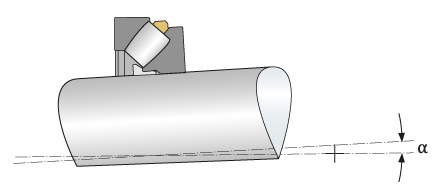
Compensation of angular misalignment in a spherical roller thrust bearing
Speed
KRW distinguishes between kinematic limiting speed nG and thermal reference speed nth. The kinematic limiting speed is a practical mechanical limit value and is based on the mechanical fatigue strength of the rolling bearing as a function of its installation situation and lubrication. The limit speed must not be exceeded even under optimum operating conditions without prior consultation with KRW.
The thermal reference speed represents the equilibrium between the heat generated in the bearing by friction and the heat flow dissipated. It is standardised in DIN ISO 15312 (Rolling bearings - Thermal reference speed).
Admissible Operating Temperatures
The admissible operating temperature of a bearing is limited by cage material, dimensional stability of the bearing components (ball race and rolling elements), as well as lubrication. By default, KRW bearings are stabilised up to 200°C (S1). KRW provides roller bearings for higher operating temperatures on request.
Dimensioning
For dynamically loaded bearings
The service life formula according to ISO 281 L10 = (C/P)p for dynamically loaded bearings requires an equivalent load (P) from constant direction and size. To calculate P, calculation factors and the ratio of axial and radial load are required.
Equivalent Dynamic Bearing Load Pa
The equivalent bearing service life for the spherical roller thrust bearings depends on the ratio Fa/Fr . The equivalent dynamic bearing load can be determined using the following formula:
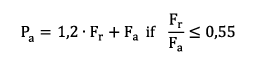
For statically loaded bearings
Dynamic dimensioning loses its validity for bearings rotating at very low speeds (n x dm ≤ 4000 mm/min). The static load safety factor S0 is calculated as follows:
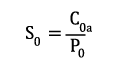
| S0 | static load safety factor | [-] |
| C0a | static load rating (from bearing chart) | [kN] |
| P0 | equivalent static bearing load | [kN] |
| n | speed | [min-1] |
| dm | mean bearing diameter [dm = (D+d)/2] | [mm] |
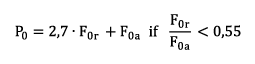
Minimum Axial Load
A minimum load is required for the reliable operation of a rolling bearing. If the minimum load is not reached, slippage may occur. Spherical roller thrust bearings are protected against slippage exclusively through a minimum axial load. The calculation for the minimum axial load for spherical roller thrust bearings is shown in the following formula: