
Cylindrical Roller Wheelset Bearings
- Cylindrical roller wheelset bearings
- Tapered roller wheelset bearings
- Spherical roller wheelset bearings

Track-bound rail vehicles represent a significant and constantly growing share in national and international transport. A high level of reliability and maximum service life are required. Safety plays a major role, especially in the area of passenger transport. Wheelset bearings are of particular importance in railway applications.
The most common types of wheelset bearings are cylindrical roller bearings. Tapered roller bearings and spherical roller bearings are also used as wheelset bearings.
KRW wheelset bearings meet the highest quality requirements. In addition to 100 % traceability of all components up to the steel melt, all parts are subjected to special non-destructive material tests. After completion, the rings and rolling elements are undergoing an ultrasonic test to detect any material defects and checked for external defects using an eddy current test. The brass or polyamide roller bearing cages to be installed are also subject to several dimensional, functional and material tests. Aware of the high level of responsibility, each individual component of the wheelset bearing is checked for internal and external errors.
After the German reunification, our company developed from a long-standing supplier to the Reichsbahn into a reliable partner of Deutsche Bahn and many railway companies in Europe and abroad. Since 1996 we have been a Q1 supplier to DB and a developer and manufacturer of wheelset bearings in the possession of manufacturer-related product qualification (HPQ).
Standards
The main dimensions of cylindrical roller bearings are standardized in DIN 5412-11 (Rolling bearings - Cylindrical roller bearings - for railway vehicles axle boxes), DIN 616 (Rolling bearings - Dimensions - General plans) and ISO 15 (Rolling bearings - Radial bearings - Boundary dimensions, general plan). The dimensions of the separate thrust collars are defined according to DIN 5412-1 (cylindrical roller bearings - separate thrust collars) and ISO 246 (cylindrical roller bearings - separate thrust collars).
Cylindrical roller wheelset bearings are specially standardised in DIN EN 12080. The greases used conform to DIN EN 12081. All wheelset bearings are tested according to customer requirements according to DIN EN 12082.
Bearing Design
Cylindrical roller wheelset bearings are separable, non-self-retaining bearings that can appear in different designs. The bearing designs differ in the number and arrangement of the ribs.
The most common design combination is WJ and WJP. In addition, two WJ bearings are rarely combined or WJ with WU+HJ separat thrust collar.
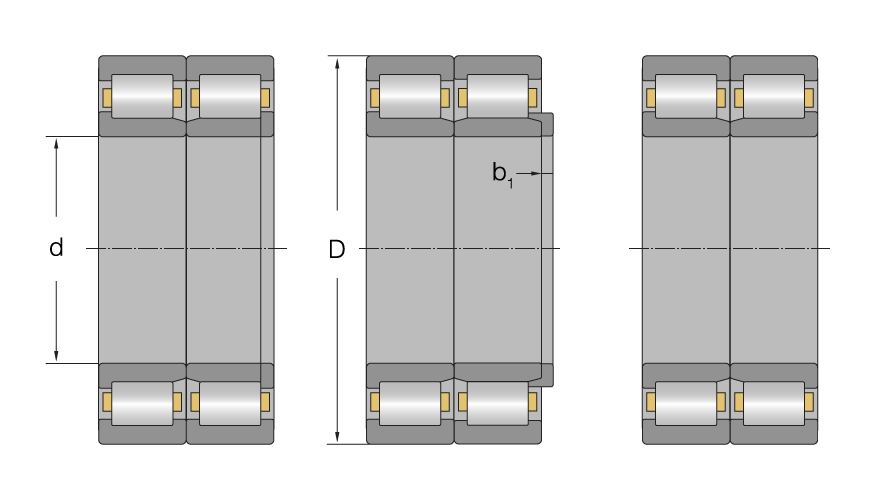
Design combinations for axle box bearings - left WJ-WJP design, centre WJ-WU+HJ designs, right WJ-WJ design
WJ bearings have two fixed ribs on the outer ring and one fixed rib on the inner ring.
WU bearings have two fixed ribs on the outer ring. The inner ring is ribless. By mounting a separate thrust collar (HJ) in WU bearings, the bearings can be combined to support bearings.
WJP bearings have two fixed ribs on the outer ring and a loose rib disc on the inner ring.
Cylindrical roller wheelset bearings can be supplied with cylindrical or tapered bore. In addition to the standardised gradients 1:12 and 1:30, the tapered bores also include the K4 cones used by the Deutsche Reichsbahn.
Bearing Clearance
Cylindrical roller wheelset bearings are supplied by KRW as standard in accordance with DIN 620-4 and ISO 5753 (radial bearing clearance) in the standard clearance (C4), but are also available in all clearance classes with restricted clearance or special clearance.

Cage
At KRW, cylindrical roller wheelset bearings are equipped as standard with a one-piece, roller-guided glass fiber reinforced window cage (suffix: TVP) or with a solid brass cage (M3). Other cage designs are available on request or are selected for specific applications and marked accordingly on the bearing.
Suffixes
Speed
KRW distinguishes between kinematic limiting speed nG and thermal reference speed nth. The kinematic limiting speed is a practical mechanical limit value and is based on the mechanical fatigue strength of the rolling bearing as a function of its installation situation and lubrication. The limit speed must not be exceeded even under optimum operating conditions without prior consultation with KRW.
The thermal reference speed represents the equilibrium between the heat generated in the bearing by friction and the heat flow dissipated. It is standardised in DIN ISO 15312 (Rolling bearings - Thermal reference speed).
Admissable Operating Temperatures
The permissible operating temperature of a bearing is limited by the cage material, the dimensional stability of the bearing components (races and rolling elements) and the lubricant. KRW bearings are dimensionally stabilised up to 200 °C as standard (S1). On request, KRW can also supply rolling bearings for higher operating temperatures.
Dimensioning
The dimensioning of cylindrical roller wheelset bearings corresponds to the dimensioning of single row cylindrical roller bearings.



